Pine Pollen: A Phytotherapeutic Treasure Rooted in History and Supported by Modern Academic Research
Pine Pollen's journey from a revered medicinal substance in ancient China to a globally recognized health supplement is a testament to the enduring wisdom of traditional medicine. Documented over 1500 years ago in the Xin Xiu Ben Cao (Tang Materia Medica, the first official Materia Medica of China, Pine Pollen has consistently held a significant place in Chinese medicinal practices.
Its historical prominence is further highlighted in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Farmer's Classic of Materia Medica, a foundational text from the Qin and Han dynasties. This comprehensive work, documenting numerous medicinal substances, including Pine Pollen, underscores its considerable therapeutic properties.
The Xin Xiu Ben Cao, an evolved version of the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing refined by classical medical experts, further cements Pine Pollen's status. As China's first official medical text, predating Western medical texts by nearly 900 years, it solidifies Pine Pollen's long-standing recognition as a valuable medicinal resource.
In classical Chinese medicine, Pine Pollen is revered as a potent tonic herb, nourishing multiple organs and systems and aligning with the Five Elements model and Five Spirits. It serves various roles, such as supporting immune function and promoting healthy skin as a Lung tonic (Metal Element, Po Spirit), enhancing endocrine balance and reproductive health as a Kidney tonic (Water Element, Zhi Spirit), and contributing to liver health and emotional equilibrium as a Liver tonic (Wood Element, Hun Spirit). Additionally, as a Heart tonic (Fire Element, Shen Spirit), it benefits cardiovascular health and nurtures spiritual aspects. In contrast, as a Spleen tonic (Earth Element, Yi Spirit), it is vital for promoting essence movement, energy flow, and digestive health.
Modern research in China and globally has validated the exceptional properties of Pine Pollen. Clinical studies exploring its safety and efficacy have revealed its ability to improve vitality, enhance fertility, balance hormones, promote liver health, boost metabolism, alleviate stress, increase energy levels, improve muscle tone, and support immune function. These diverse benefits have made Pine Pollen a valuable daily supplement for overall health and well-being.
Pine Pollen's historical significance extends beyond China, influencing traditional medical practices in Japan and Korea for centuries. It has been used in Japanese culture as medicine and food, known for its anti-aging effects and beauty applications. In Korea, texts like the Dongui Bogam highlight its importance in traditional medicine.
This article delves into Pine Pollen's rich historical background and scientific research, highlighting its multifaceted benefits. By examining its traditional use and modern scientific insights, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this extraordinary natural resource. As Pine Pollen gains global attention, we aim to offer up-to-date and reliable information, empowering you to make informed decisions about incorporating this powerful natural resource into your health and wellness journey.
Historical Use of Pine Pollen in Chinese Medicine
The Deep-Rooted Significance of Pine Pollen and the Evolution of Ancient Chinese Medical Texts
The history of Pine Pollen is deeply intertwined with the earliest Chinese medical manuscripts, underscoring its vital role and exceptional properties. These seminal works not only document the medicinal uses of Pine Pollen but also reflect its enduring relevance in the rich tapestry of Classical Chinese Medicine.
The Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (神农本草经) (Qin and Han Dynasties, circa 200 C.E.)
The Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Farmer's Classic of Materia Medica) is esteemed as one of the first comprehensive Chinese medical and pharmacological manuscripts. Authored around 200 C.E., this text is a cornerstone in the history of Chinese medicine. The title "神农本草经" (Shén Nóng Běn Cǎo Jīng) translates to The Divine Farmer's Materia Medica in English, with each component of the title offering a glimpse into the text's significance:
- Shen Nong: This term is associated with the legendary figure of the Divine Farmer, a prominent entity in Chinese culture, acknowledged as the pioneer of agriculture and herbal medicine
- Ben Cao: Translated as "roots and herbs," the term "Ben Cao" typically refers to herbal medicine.
- Jing: In this context, "Jing" signifies a "classic" or "canonical text," indicating its status as a foundational work in the field.
The Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing, compiled during the Qin and Han dynasties, categorizes 365 medicinal substances, including 252 medicinal herbs, 67 animal-derived medicines, and 46 medicinal minerals. This division reflects the extensive scope of ancient Chinese pharmacology.
Significantly, the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing is the earliest pharmacological text to record the use of Pine Pollen, acknowledging its medicinal benefits and establishing its importance within Traditional Chinese Medicine. This mention in such a foundational text highlights Pine Pollen's long-standing value and its integration into the fabric of traditional healing practices.
Xin Xiu Ben Cao (新修本草) (Tang Dynasty, 618 to 907 C.E.)
The Xin Xiu Ben Cao (Xīn Xiū Běn Cǎo), also known as the Tang Materia Medica or the Newly Revised Materia Medica, emerged as a significant and authoritative medical document during the Tang Dynasty. This text represents a pivotal moment in the history of Chinese medicine, marking the culmination of centuries of refinement and growth by classical medical scholars.
As Chinese medicine continued to evolve, the foundational Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing underwent further enhancements and advancements. These efforts, led by renowned classical medical experts, resulted in the creation of the Xin Xiu Ben Cao. This work distinguished itself as China's first official medical text during the Tang Dynasty, predating Western medical texts such as the Nuremberg Pharmacopoeia by nearly nine centuries.
Building upon the knowledge and wisdom of its predecessor, the Xin Xiu Ben Cao serves as a comprehensive compendium of medicinal substances. It offers detailed information on the characteristics, applications, and preparation methods of various therapeutic resources. Pine Pollen is recognized as a crucial medicinal resource in its pages, further solidifying its importance in Chinese medicine.
The Xin Xiu Ben Cao played an instrumental role in preserving and advancing the knowledge of medicinal substances, including Pine Pollen, through subsequent dynasties. Its status as China's first official medical document and its inclusion of Pine Pollen underscore this vital tonic herb's historical recognition and ongoing relevance. The text's contribution to the field of Chinese medicine is invaluable, providing a rich source of knowledge that continues to inform modern understanding and application of traditional remedies like Pine Pollen.
Pine Pollen: Translated Citations and References from Historical Texts
The following are translated citations from various Chinese, Japanese, and Korean medical texts. These translations, provided by RAW Forest Foods LLC in collaboration with a Chinese TCM expert, offer invaluable insights into the traditional uses and perceptions of Pine Pollen. They serve not only as a bridge connecting modern audiences to ancient wisdom but also as a testament to the enduring relevance of Pine Pollen in traditional healing practices.
Tang Ben Cao (唐本草, Tang Dynasty, 657-659 C.E.)
The Tang Ben Cao (唐本草), the Tang Materia Medica, is a seminal medical text compiled during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 C.E.). This work is regarded as a significant milestone in developing Traditional Chinese Medicine. It offers comprehensive insights into various medicinal substances, including Pine Pollen. Pine Pollen is meticulously documented within its pages, providing a thorough understanding of its properties, uses, and potential health benefits. The Tang Ben Cao remains a vital resource in Traditional Chinese Medicine, contributing to the knowledge and application of Pine Pollen alongside other medicinal substances. Tang Ben Cao states that:
Pine Pollen is also named Pine Yellow because it resembles cattail pollen. Long-term use of Pine Pollen may decrease weight (assist in weight loss). The medicinal application is greater than the use of Pine Bark, Pine Leaf, and Pine Resin.
Ben Cao Yan Yi (本草衍义, Song Dynasty, 1116 C.E.)
The Ben Cao Yan Yi (本草衍义), also known as The Expanded Herbal Foundation, is a renowned herbal text from the Song Dynasty (960-1279 C.E.). This text is celebrated for its extensive knowledge of herbal medicine and provides valuable insights into Pine Pollen. It elucidates the unique characteristics and diverse medicinal applications of Pine Pollen, making it an indispensable resource for understanding its role and utility within traditional Chinese medicine. Ben Cao Yan Yi states that:
The yellow powder of the pine flower is called pine yellow. People in the mountainous areas collect the pollen at specific times and use it in the preparation of a delicious pastry. However, because Pine Pollen could not be preserved for any great length of time, it was seldom transported to distant places. Pine yellow (Pine Pollen) looks like cattail pollen but with a lighter taste. Pine yellow (Pine Pollen) can treat postnatal high fever, headache, dry mouth and lips, agitation, thirst, and muddled and unpleasant moods, too.
Ben Cao Gang Mu (本草纲目, Ming Dynasty, 1590 C.E.)
Compiled by Li Shizhen during the Ming Dynasty, the Ben Cao Gang Mu (Compendium of Materia Medica) stands as one of the most comprehensive materia medica texts in Chinese history. It delves into various medicinal substances, including Pine Pollen, providing detailed insights into its properties, uses, and potential benefits. This text remains a crucial reference in Traditional Chinese Medicine, enhancing our understanding of Pine Pollen and its medicinal applications. Ben Cao Gang Mu states that:
Pine Pollen has a sweet, mild taste, with no toxicity. It assists the cardiopulmonary system (heart and lungs), nourishes Qi, expels wind, stops bleeding, and can be used for brewing into wine.
Ben Cao Cong Xin (本草从新, Qing Dynasty, 1757 C.E.)
The Ben Cao Cong Xin (New Compilation of Materia Medica), a significant Qing Dynasty contribution, offers valuable insights into the therapeutic uses of Pine Pollen. This text is vital for understanding Pine Pollen's properties and applications in Traditional Chinese Medicine. According to the Ben Cao Cong Xin:
Pine Pollen is effective to cure several conditions of variola, sores, injuries, as well as rotten [gangrene] wounds which will not scab on their own.
Jing Bian Ben Cao Gang Mu (景辩本草纲目, Revised 2010)
The Concise Compendium of Materia Medica, an updated edition published in 2010, is an abridged and modernized version of the monumental work of Ben Cao Gang Mu, initially authored by the renowned herbalist Li Shizhen. This contemporary rendition aims to encapsulate essential information on a wide array of medicinal substances, including a detailed account of the healing properties of Pine Pollen.
In the Jing Bian Ben Cao Gang Mu, Shizhen Li describes the Pine tree as tall and straight, with rough and thick bark like fish scale, which blooms during February and March from a 4 inch to 5 inch flower (the male pine catkin). Li refers to Pine Pollen as Pine yellow, and the pine cone as being shaped like a pig's heart.
Li describes the taste of Pine Pollen (Pine yellow) as sweet and mild with no toxicity. According to Li, Pine Pollen nourishes the Heart and Lung, tonifies Qi, expels wind, and stops bleeding (hemorrhaging).
Chinese Pharmacopoeia (中国药典, 1985)
The Chinese Pharmacopoeia is an official document establishing standards and specifications for medicinal substances used in China. The 1985 edition provides detailed information on the identification, properties, and uses of Pine Pollen and other therapeutic substances. It is a comprehensive reference for Traditional Chinese Medicine practitioners, pharmacists, and researchers.
The characteristics, properties, and potential therapeutic applications of Pine Pollen are thoroughly described in the 1985 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. This valuable resource ensures consistency and quality in producing and using medicinal substances, including Pine Pollen, within Traditional Chinese Medicine.
According to the 1985 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia:
- Pine Pollen is the dried pollen collected from the fringes of Pinus massoniana lamb. Pinus tabulaeformis carr., and Pinus yunnanensis franch. trees during their spring bloom.
- Characteristics: It is a light yellow fine powder with a lightweight, odorless, and smooth texture.
- Identification: Under a microscope, RAW Pine Pollen appears as elliptical cells with a length of 45-55 micrometers and a diameter of 29-40 micrometers. The surface is smooth, with inflated gasbags on both sides, exhibiting a reticular texture and polygonal mesh shape.
- Properties: Pine Pollen is sweet and mild and acts on the Liver and Spleen meridians.
- Main functions: It eliminates dampness, has astringent and hemostatic properties, and aids in treating eczema, impetigo, skin erosion, dripping ichor, traumatic bleeding, and diaper-induced dermatitis.
- Usage and dosage: For external use only.
- Shelf life: Store in a dry place away from moisture.
Detailed Explanation of 800 Kinds Chinese Medicine (2009)
The Detailed Explanation of 800 Kinds Chinese Medicine provides comprehensive information on medicinal substances, including Pine Pollen. It offers detailed insights into its characteristics, sourcing, and medicinal properties.
- Name: Pine Pollen, Pine Pollen Flower, Pine Yellow.
- Source: Mainly obtained from trees of Pinus massoniana lamb., Pinus tabulaeformis carr., and Pinus yunnanensisfranch. in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Liaoning, Jilin, Hubei, and Yunnan Provinces.
- Collection and processing: Pine catkins are collected when pine trees bloom in April and May. They are then naturally dried to remove impurities.
- Specification and characteristics: Pine Pollen is a light yellow fine powder composed of tiny round cells. It is lightweight, easily lifted in the air, feels smooth, floats in water, has a faint smell, and tastes mild. High-quality Pine Pollen is characterized by its yellow color, delicate and soft pollen, absence of impurities, and excellent fluidity.
- Identification: Under a microscope, RAW Pine Pollen appears as elliptical cells with a length of 45-55 micrometers and a diameter of 29-40 micrometers. The surface is smooth, with inflated gasbags on both sides, exhibiting a reticular texture and polygonal mesh shape.
- Properties: Pine Pollen is sweet and mild and acts on the liver and spleen. It tonifies the spleen and liver yang, nourishes the liver, eliminates wind, and has astringent and hemostatic properties.
These translated citations offer valuable historical insights into the traditional use of Pine Pollen and further validate its reputation as a valued remedy in ancient Chinese, Japanese, and Korean medicine.
Historical and Contemporary Use of Pine Pollen in Japan and Korea
Cultural Influence: Pine Pollen's Journey into Japanese and Korean Medicine
With its rich history and therapeutic properties, Pine Pollen has significantly influenced traditional medicine in Japan and Korea. Its cultural impact has shaped its historical significance and continues to affect its contemporary use.
Historical Significance in Japan: From Royalty to Popular Consumption
In Japan, Pine Pollen's history stretches back to ancient times when it was highly revered, especially among royalty and the aristocracy due to its scarcity. Over time, it became more accessible and gained popularity as a natural health enhancer among the general population.
Scientific Discoveries: Anti-Aging Effects and Beauty Applications in Japan
Recent scientific research in Japan has uncovered Pine Pollen's anti-aging effects and potential in beauty and skincare. Studies indicate that its antioxidants and phytochemicals can protect the skin from oxidative stress, reduce wrinkles, and improve skin health, leading to its inclusion in various beauty products and supplements.
Pine Pollen in Korean Medicine: The Dongui Bogam and Its Lasting Impact
In Korean traditional medicine (Hanbang), Pine Pollen holds a significant place, as evidenced in the Dongui Bogam, an influential medical text by the esteemed physician Heo Jun during the Joseon Dynasty. This text provides detailed insights into Pine Pollen's therapeutic properties and applications for various health conditions.
Treasured Tradition: Pine Pollen's Use and Appreciation in Korea's Joseon Dynasty
During the Joseon Dynasty, Pine Pollen was highly valued for its medicinal properties and nutritional benefits. It was a key ingredient in formulations aimed at enhancing vitality, physical endurance, and overall well-being, reflecting its esteemed status in Korean culture and traditions.
The historical and contemporary use of Pine Pollen in Japan and Korea demonstrates its lasting presence in traditional medicine and cultural practices. The continued appreciation of Pine Pollen's therapeutic potential is passed down through generations, affirming its role as a revered natural resource in these countries.
The Enduring Significance of Pine Pollen in Classical and Traditional Chinese Medicine
Pine Pollen, known as 松花粉 (Sōnghuā fěn) in Chinese, holds a distinguished place in the annals of Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM) and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). With a history that traces back to ancient texts, this natural substance is not just an herb but a potent tonic with a multitude of therapeutic properties. It is highly esteemed in these ancient healing traditions for its adaptogenic and tonic qualities, cherished for its ability to nourish and fortify specific organs or bodily systems, and its unique capacity to help the body adapt to various stressors, promoting equilibrium and resilience.
In the classical framework of Chinese medicine, Pine Pollen aligns with the principles of Yin-Yang balance and the harmonization of the Five Elements (Wu Xing) with human physiology. Each organ system, associated with a specific element and spirit, benefits from Pine Pollen's nurturing capabilities. Celebrated for its extensive tonifying effects, Pine Pollen exerts a significant influence on multiple facets of human health. It is a crucial component in numerous herbal formulations, prized for its harmonizing effects on the body's vital energy (Qi), its ability to enrich essence (Jing), and its calming influence on the spirit (Shen).
In contemporary wellness practices, Pine Pollen continues to be recognized for its adaptogenic and tonic attributes. Regarded as a nutritional powerhouse, it is packed with vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes, and bioactive compounds, enabling it to act synergistically to bolster vital functions and foster overall health and well-being. Beyond its role as a supplement, Pine Pollen has gained recognition as a functional food, offering medicinal benefits while serving as a dense nutritional source. Its restorative and nourishing characteristics contribute to enhancing immune system strength, improving endocrine function, promoting skin health, and supporting longevity and vitality.
Within CCM and TCM, Pine Pollen is frequently used to rectify imbalances in Yin and Yang, and to replenish the Five Zang organs (heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys). Its adaptogenic properties are especially valued for addressing stress-induced imbalances, often perceived as disturbances in the harmonious circulation of Qi and blood. The enduring use of Pine Pollen in both CCM and TCM underscores its therapeutic versatility and the profound wisdom embedded in ancient healing practices, embodying the core principles of harmony and balance in Chinese medical philosophy.
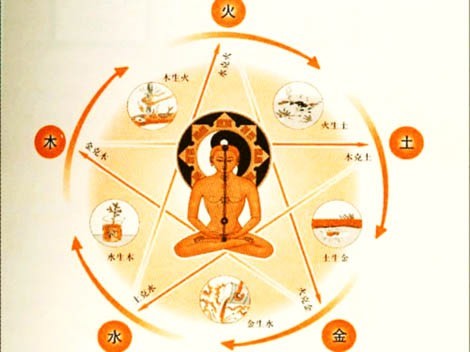
Pine Pollen in the Classical and Traditional Chinese Medicine Model
Integrating Pine Pollen's Tonic Effects within the Five Elements and Zang Fu Organ Systems in Classical and Traditional Chinese Medicine
In Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM) and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the Five Elements model and the Zang Fu organ systems offer a comprehensive framework to understand the complex interplay between natural forces and human health. This model categorizes each season, organ system, and spirit according to the Five Elements: Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.
Pine Pollen is celebrated for its adaptogenic and tonic properties, stemming from its capacity to nourish the Zang Fu organs. This nourishment contributes to a wide array of health benefits and the potential to enhance overall well-being. Its extensive fortifying effects on key organ systems, including the Lungs, Kidneys, Liver, Heart, and Spleen, underscore its vital role in maintaining the body's harmonious balance. This holistic view positions Pine Pollen as a versatile and potent healing herb in both CCM and TCM, offering deep insights into its therapeutic actions and potential.
- Wood Element (Liver and Gallbladder, Hun Spirit): Pine Pollen, associated with the Wood element, nourishes the Liver and Gallbladder. It facilitates the smooth flow of Qi, essential for digestive health, and bolsters decision-making and courage. By fortifying these organs and enriching the Hun (Ethereal Soul), Pine Pollen supports life direction, dreams, and inspirations, thus maintaining the Wood element's equilibrium.
- Metal Element (Lungs, Po Spirit): Valued for its lung-moistening properties in CCM and TCM, Pine Pollen enhances respiratory health and fortifies the body's Wei Qi (defensive energy). This effect strengthens the immune system and is believed to improve skin health, mirroring the Metal Element's protective nature and the lung-skin connection. It may also provide relief from respiratory ailments.
- Water Element (Kidneys, Zhi Spirit): As a kidney tonic, Pine Pollen aids in maintaining endocrine balance, reproductive health, and the sustenance of Jing (essence), crucial for vitality and longevity. It is recognized for enhancing fertility, hormonal equilibrium, and promoting longevity. Pine Pollen also supports the kidneys' role in cognitive functions, hair vitality, and bone strength, reflecting their foundational energy in the body.
- Fire Element (Heart, Shen Spirit): Pine Pollen, beneficial for the heart, potentially assists in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and supporting cardiovascular functions. It nurtures the Shen (spirit), highlighting the heart's pivotal role as the ruler of the organs, overseeing mental and emotional processes.
- Earth Element (Spleen, Yi Spirit): Essential for the spleen, Pine Pollen aids in transforming and transporting Gu Qi (food essence) and ensuring smooth Qi circulation. It bolsters digestive processes and strengthens the gastrointestinal system, thereby enhancing overall vitality and well-being. This underscores the spleen's critical role in Qi and Blood production.
By integrating Pine Pollen into health practices, we tap into the ancient wisdom of CCM and TCM, harnessing its potential to support and balance various aspects of our health. This approach underscores the enduring relevance and adaptability of traditional medicinal knowledge in contemporary wellness contexts.
Translating the Tonic Effects of Pine Pollen: A Comprehensive Traditional and Modern Perspective
Pine Pollen, widely recognized in Classical Chinese Medicine (CCM) and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), is renowned for its extensive tonic properties. This section interprets the uses of Pine Pollen in Chinese Medicine, integrating our contemporary understanding of phytotherapeutic herbal medicine, functional foods, and adaptogenic and tonic herbs:
- Respiratory Health: Pine Pollen's lung-moistening properties support respiratory health, a crucial aspect in CCM for maintaining overall vitality.
- Pain Relief: Its potential anti-inflammatory properties may provide relief from rheumatic and arthritic pain, aligning with the common characteristics of adaptogens
- Fatigue and Endurance: Believed to alleviate fatigue and enhance physical endurance, Pine Pollen resonates with the adaptogenic principle of bolstering the body's stress resistance.
- Immune System Regulation: It contributes to regulating and strengthening the immune system, a benefit increasingly acknowledged in functional wellness.
- Skin Health: The rich nutritional profile of Pine Pollen aids in skin rejuvenation and health, improving skin quality and appearance, and may help in managing acne and age spots.
- Cardiovascular Support: Supporting heart health and aiding in cholesterol management, Pine Pollen is beneficial for cardiovascular wellness.
- Digestive Health: Enhancing gastrointestinal health and digestion, Pine Pollen is integral to both CCM and modern functional medicine for overall health maintenance.
- Cognitive Function: Its potential antioxidant properties and nutrient density are believed to promote brain health and cognitive function. Additionally, Pine Pollen’s adaptogenic effects can enhance mental clarity and focus, improving attention span and brain function.
- Prostate Health: Supporting reproductive health and hormonal balance, Pine Pollen provides relief from prostate-related issues.
- Motor Skills and Agility: Beneficial for athletes and those seeking physical performance enhancement, Pine Pollen improves gross motor skills and agility.
- Weight Management: It may influence metabolic processes, facilitating healthy weight management.
- Overall Health and Immunity: Pine Pollen is used to promote overall health and enhance immune function, key in holistic health approaches.
- Post-Workout Recovery: Valued in sports nutrition and functional wellness, it assists in post-workout recovery and fitness restoration.
- Cellular Detoxification: Supporting gentle daily cellular detoxification, Pine Pollen aligns with contemporary efforts to reduce the body's toxic load.
- Anti-Aging Effects: Pine Pollen's role in enhancing skin elasticity and offering anti-aging benefits makes it a valuable asset in both traditional practices and modern anti-aging strategies.
The tonic effects of Pine Pollen provide various health benefits, highlighting its potential as a versatile natural remedy within the framework of CCM and TCM. Both traditional wisdom and contemporary research support Pine Pollen's valuable role in promoting holistic well-being.
Clinical Investigations into Pine Pollen: A Comparative Analysis of Chinese and Western Studies
Deciphering the Scientific Evidence: The Efficacy of Pine Pollen as a Supplement
Pine Pollen has attracted attention from scientific communities in both China and the West, leading to numerous studies investigating its potential as a robust natural supplement. These studies focus on Pine Pollen's safety, efficacy, and health benefits, substantiating its traditional use through systematic research.
In China, Pine Pollen is integral to traditional medicine, prompting extensive research into its effectiveness and safety. Western research, meanwhile, has increasingly recognized Pine Pollen as a potent adaptogenic phyto-therapeutic, focusing on its bioactive components and their physiological effects.
Research Outcomes: Pine Pollen's Impact on Vitality, Hormonal Health, and Wellness
- Vitality and Stamina: Clinical research in China demonstrates Pine Pollen's ability to enhance vitality and stamina significantly.
- Hormone Levels and Ratios: Studies show Pine Pollen's effectiveness in balancing hormones, particularly in males, by increasing testosterone levels and improving fertility. It also helps stabilize the estrogen-to-testosterone ratio in both sexes.
- Liver Health and Detoxification: Pine Pollen is suggested to stimulate liver cell activity, aiding in detoxification.
- Metabolic Regulation and Weight Management: Research indicates Pine Pollen's role in metabolism modulation, contributing to weight management.
- Immune Function: Pine Pollen exhibits immunomodulatory properties, enhancing immune response.
Pine Pollen: A Phytotherapeutic Asset Validated by Clinical Research
The extensive research from China and the West underscores Pine Pollen's multifaceted nature as a natural phyto-therapeutic agent. It is renowned for enhancing vitality, hormonal balance, liver health, metabolism, and immune function.
These investigations validate Pine Pollen's traditional uses and expand our understanding of its role in holistic wellness. While current research establishes Pine Pollen as a promising phytotherapeutic agent, further studies are needed to explore its full potential and mechanisms of action.
Therapeutic Advantages of Pine Pollen
Pine Pollen: A Reservoir of Antioxidants for Cellular Protection and Oxidative Stress Mitigation
Pine Pollen is renowned for its exceptional antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. These reactive molecules are known to contribute to cellular dysfunction, inflammation, and various health disorders. The rich array of antioxidants in Pine Pollen, including flavonoids, phenolic compounds, and vitamin E, helps neutralize these harmful free radicals, reducing the risk of oxidative stress and promoting cellular health.
Scientific studies confirm that Pine Pollen is abundant in potent antioxidants. These compounds are instrumental in combating oxidative stress, thereby enhancing overall wellness and potentially preventing age-related diseases and chronic health conditions.
Pine Pollen is renowned for its exceptional antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. These reactive molecules are known to contribute to cellular dysfunction, inflammation, and various health disorders. The rich array of antioxidants in Pine Pollen, including flavonoids, phenolic compounds, and vitamin E, helps neutralize these harmful free radicals, reducing the risk of oxidative stress and promoting cellular health.
Scientific studies confirm that Pine Pollen is abundant in potent antioxidants. These compounds are instrumental in combating oxidative stress, thereby enhancing overall wellness and potentially preventing age-related diseases and chronic health conditions.
Pine Pollen's Anti-Inflammatory Capacity: Reducing Inflammation and Encouraging Wellness
Chronic inflammation is implicated in a wide range of health issues, from cardiovascular diseases to arthritis and certain forms of cancer. Pine Pollen exhibits significant anti-inflammatory properties, which may play a role in reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
Research indicates that Pine Pollen is rich in bioactive compounds, such as phenols and proanthocyanidins, known for their potent anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds can inhibit inflammatory pathways and decrease the production of pro-inflammatory molecules in the body. By modulating the inflammatory response, Pine Pollen may offer relief from symptoms associated with inflammation-related conditions and contribute to a healthier inflammatory balance.
Deciphering Pine Pollen's Mode of Operation: The Active Compounds in Pine Pollen
Pine Pollen's health benefits are rooted in its complex and varied phytochemical makeup. Let's delve into the key active ingredients found in Pine Pollen and their roles:
- Phyto-androgens: Unique to Pine Pollen, these plant-based substances resemble human androgens like testosterone in structure and function. Pine Pollen contains phyto-androgens such as androstenedione, androsterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and testosterone. While their concentrations are relatively low compared to pharmaceutical sources, they are thought to produce mild androgenic effects in the body. These phyto-androgens can contribute to hormonal balance, increased vitality, and enhanced well-being. For a detailed exploration of Pine Pollen's phyto-androgenic properties, consider reading the article, "Pro-Androgenic and Adaptogenic Effects of Pine Pollen."
- Antioxidants: Pine Pollen is abundant in antioxidants, including flavonoids, phenolic compounds, and vitamin E. These antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage, and potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Amino Acids: Containing a wide array of amino acids, including essential ones that the body cannot synthesize, Pine Pollen supports various physiological functions. These amino acids are vital for muscle repair, immune function, and hormone synthesis.
- Vitamins and Minerals: As a natural source of essential vitamins and minerals, Pine Pollen provides nutrients crucial for health. It includes vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, folate, and vitamin E, along with minerals like zinc, selenium, copper, and magnesium. These contribute to energy production, immune function, and cellular metabolism.
- Plant Sterols: Pine Pollen contains plant sterols such as beta-sitosterol, campesterol, and stigmasterol, which are associated with heart health, cholesterol management, and prostate health benefits.
- Enzymes: The variety of enzymes in Pine Pollen, including amylase, protease, and lipase, aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. These enzymes facilitate the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, enhancing digestive efficiency and nutrient uptake.
Pine Pollen’s Active Compounds In Action:
- Hormonal Modulation: Pine Pollen's phyto-androgens can interact with hormone receptors in the body, potentially influencing hormone production and regulation. These interactions may modulate testosterone levels, contributing to hormonal balance. Such effects could lead to improved vitality, reproductive health, and overall hormonal equilibrium.
- Immune Modulation: Pine Pollen has been observed to modulate immune function by enhancing the activity and responsiveness of immune cells. This may result in a strengthened immune system, bolstered defenses against pathogens, and overall enhanced immune functionality.
- Anti-Inflammatory Action: The anti-inflammatory properties of Pine Pollen play a significant role in reducing bodily inflammation. By modulating inflammatory pathways and decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, Pine Pollen can help maintain a healthier inflammatory balance, potentially alleviating symptoms associated with various inflammatory conditions.
- Antioxidant Protection: Rich in antioxidants, Pine Pollen offers crucial protection against oxidative damage to cells. These antioxidants neutralize free radicals, preventing oxidative stress and thereby supporting cellular health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Nutritional Support: Pine Pollen's nutrient-dense profile provides essential vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and enzymes, supporting a range of bodily functions. These nutrients contribute to holistic well-being, aiding in energy production and maintaining vital physiological processes.
- Prebiotic Effects: Recognized for its prebiotic properties, RAW Pine Pollen acts as a nourishing substrate for beneficial gut bacteria. By supporting these microbes, Pine Pollen can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and overall health. The prebiotic impact of Pine Pollen thus plays a role in promoting optimal gut health.
The diverse and interconnected mechanisms of Pine Pollen, encompassing phyto-androgens, antioxidants, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, plant sterols, enzymes, and prebiotic properties, contribute to its therapeutic efficacy. These attributes position Pine Pollen as a valuable natural resource for enhancing health and vitality and supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
Possible Effects of Pine Pollen on Testosterone and Estrogen
Maintaining healthy hormone levels is essential for optimal health and wellness. Pine Pollen has gained recognition for its potential role in supporting hormonal balance, particularly in relation to testosterone and estrogen levels.
Research indicates that Pine Pollen may positively influence testosterone production and regulation in men. It has been shown to enhance testosterone synthesis, increase sperm count, and improve fertility. Additionally, Pine Pollen is reported to balance the estrogen-to-testosterone ratio in both men and women, aiding in overall hormonal harmony.
Moreover, Pine Pollen contains phytohormones such as brassinosteroids, which may have a regulatory effect on hormone signaling pathways. These plant-derived hormones, structurally akin to human hormones, could play a role in modulating hormonal activities, contributing to overall hormonal balance and wellness.
Pine Pollen's Role in Managing Specific Health Conditions: Insights into Prostate Health, Immune Function, and Skin Health
- Prostate Health: Traditionally used for its potential benefits in promoting prostate health, Pine Pollen may aid in maintaining prostate wellness by reducing inflammation, inhibiting cell proliferation in the prostate, and supporting healthy hormonal balance. It may also be beneficial in preventing and managing prostate-related conditions.
- Immune Function: Pine Pollen is renowned for its immunomodulatory properties, enhancing the immune system's capabilities. It has been observed to stimulate immune cell activity, bolster immune responses, and increase antibody production. By fortifying immune function, Pine Pollen may help protect against infections, enhance immune defenses, and improve overall immune health.
- Skin Health: The benefits of Pine Pollen extend to skin health as well. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, combined with a rich nutrient profile, make it a valuable component in skincare products. Pine Pollen is known to improve skin elasticity, diminish the appearance of wrinkles and age spots, and promote a youthful complexion. It may also be effective in alleviating specific skin conditions, such as acne and dermatitis.
Future Research Directions
Unveiling New Horizons: Areas for Further Investigation in Pine Pollen Research
While Pine Pollen has a rich historical and cultural background, as well as promising scientific findings, there are still many avenues of research that can contribute to our understanding of its full potential. Here are some areas for further investigation in Pine Pollen research:
- Mechanisms of Action: Despite our current knowledge about the phytochemical composition and potential health benefits of Pine Pollen, further studies are needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which it exerts its effects on the body. Understanding the molecular pathways and biological interactions of Pine Pollen's active compounds can provide valuable insights into its therapeutic properties.
- Clinical Trials: Conducting well-designed clinical trials can provide more robust evidence regarding the efficacy and safety of Pine Pollen in specific health conditions. Large-scale, randomized controlled trials with diverse populations can help validate its effects on hormonal balance, immune function, and other targeted health outcomes.
- Comparative Studies: Comparative studies between different species of pine trees and geographical regions can shed light on potential variations in the phytochemical composition and health benefits of Pine Pollen. Exploring the differences between pine species and their impact on therapeutic properties can provide valuable insights for optimizing its use.
- Synergistic Effects: Investigating the potential synergistic effects of Pine Pollen with other natural compounds or therapeutic modalities can open up new possibilities for integrative approaches to health and well-being. Understanding how Pine Pollen interacts with other herbs, nutrients, or lifestyle interventions can enhance its therapeutic potential.
- Long-Term Safety: Long-term studies assessing the safety profile of Pine Pollen over extended periods are essential for determining its suitability for prolonged use and potential side effects that may arise over time. This research can contribute to establishing appropriate guidelines for long-term supplementation with Pine Pollen.
- Standardization and Quality Control: Establishing standardized methods for the extraction, processing, and quality control of Pine Pollen products is crucial to ensure consistency and reliability. Research focusing on developing quality standards and authentication methods can help consumers make informed choices and ensure product integrity.
By addressing these areas of research, we can deepen our understanding of Pine Pollen and unlock its full potential as a natural therapeutic agent. Continued scientific exploration and collaboration will contribute to the growing body of knowledge surrounding Pine Pollen and its role in promoting health and well-being.
Conclusion: Pine Pollen is an Ancient Remedy Supported by Modern Research
Pine Pollen stands as a remarkable phytotherapeutic agent, boasting a rich historical background and robust scientific support. Its use in Classical Chinese Medicine and historical significance in Japan and Korea highlight its long-standing recognition for healing properties. Modern scientific studies further validate its health benefits and enhance our understanding of its mechanisms.
Embracing the Potential: From Historical Wisdom to Contemporary Applications
Exploring Pine Pollen's historical use and modern applications reveals its multifaceted nature and potential for enhancing well-being. Recognized as a potent adaptogenic and tonic herb, Pine Pollen offers hormone balancing, specific health condition support, and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits
While Pine Pollen continues to intrigue, further research is essential to unlock its full potential. Future studies could reveal additional health benefits, novel therapeutic applications, and deepen our understanding of its actions.
In our quest for optimal health, Pine Pollen represents the convergence of ancient wisdom and modern scientific inquiry. With its rich heritage and promising future, Pine Pollen invites us to explore its transformative power as a natural remedy.
Disclosures
Disclosures
Before making any changes to your diet or health regimen, including the use of dietary or nutritional supplements, we strongly recommend consulting with a healthcare practitioner. This advice is particularly relevant if you are pregnant, nursing, under the age of 18, have any known allergies, or have any pre-existing medical conditions.
At RAW Forest Foods, we are committed to your health and well-being. It is important to understand that our products are dietary supplements, not pharmaceuticals. We endeavor to provide high-quality supplements, but please be aware:
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Ingredient Transparency and Allergen Awareness
Your safety and health are paramount. We strive to provide detailed ingredient information for each of our products to help you make informed choices. It is crucial not to consume any product containing ingredients to which you have, or suspect you may have, an allergy. Allergic reactions can be severe and, in some cases, life-threatening.
Interaction with Medications
If you are currently taking any medications, it is crucial to discuss potential interactions with your healthcare provider. Dietary supplements can interact with medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or leading to adverse effects.
Consult our full Terms and Conditions for additional information.